
Bacteria can be found in plaque, a byproduct of food, saliva, and bacteria in the mouth. Plaque adheres to teeth, harming them and the gums. If plaque is not cleaned through regular and effective brushing and flossing, bacteria can spread inside the soft tissue of the gums which, in turn, will allow an abscess to develop.
Tooth abscess affects 4,800 Canadians. A toothache can be excruciating, and it’s the most common indicator of a tooth infection. It’s advisable to schedule an appointment with your dentist immediately. Anyone, young or old, can get one. The longer you wait, the more likely the infection will spread to other teeth and tissues.
What Is Dental Abscess?
A tooth abscess is a collection of pus inside the teeth or gums. The abscess is usually caused by a bacterial infection, which has built up in the tooth’s soft pulp. Abscesses can develop in various locations around a tooth for a variety of reasons, affecting not just the tooth but also the surrounding bone and, in some cases, neighbouring teeth.
Types of Dental Abscess
Abscesses can be caused by 3 types of tooth infections:
- Gingival Infection
This infection occurs in the gums. It normally has little effect on the tooth or its supporting structures.
- Periapical Infection
An infection at the root’s tip is called a periapical abscess. This happens when germs enter the tooth through a crack or cavity and spread to the pulp. The pulp is the tooth’s deepest layer, which contains nerves and blood vessels. When bacteria infect the pulp, they can travel to the end of the tooth’s root, triggering the infection to extend to the bone and ultimately result in an abscess.
- Periodontal Infection
This infection begins in the bone and connective tissues that support the tooth. Periodontal abscesses are more common in adults and are caused by periodontitis or gum disease.
Symptoms of Dental Abscess
If it develops, it is frequently accompanied by strong, throbbing pain, particularly when you apply pressure to your teeth, but not always. It may also spread to your jaw or other regions of your face on the affected side.
Other signs and symptoms of a dental abscess include:
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Breathing or swallowing difficulties
- Fever
- Inflammation
- Pus in your teeth
- Redness of the gums
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Temperature sensitivity
An abscess can occasionally develop a pimple-like bump on your gum. If you squeeze it and liquid comes out, that substance is pus and you have an abscessed tooth.
Go to the hospital if you have facial swelling, fever, or difficulty breathing or swallowing. The infection may have progressed to other places of your body.
Causes of Dental Abscess
A tooth infection can be caused by anything that allows germs to enter the tooth or surrounding tissues.
Among the causes are:
- Severe dental decay
A cavity, also known as tooth decay, is the destruction of the tooth’s hard surfaces. This happens when bacteria break down sugars in food and drinks, producing acid that destroys the enamel. Bacteria can enter any opening in a tooth and spread to the pulp if it is broken, chipped, or cracked.
- Periodontitis
Periodontitis, or gum disease, is an infection and inflammation of the tissues around the teeth. Bacteria get access to deeper tissues as gum disease worsens.
- Tooth Injury
Even if there is no visible crack, trauma to the tooth can cause injury to the inner pulp. Because of the injury, it is more vulnerable to infection.
Complications
Complications develop in a vast majority of cases if the abscess is not treated.
These could include:
- Dental cysts
A dental cyst or a fluid-filled cavity may form at the bottom of the root of the tooth if the abscess is left untreated. The cyst has a significant chance of becoming infected. If this occurs, antibiotics and even surgery may be required.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
This is an extremely rare complication. A blood clot forms at the cavernous sinus, a major vein at the base of the brain, as a result of germs spreading. Antibiotics and, sometimes, sinus surgery may be necessary to treat it. In some circumstances, this condition could even be lethal.
- Ludwig’s angina
When the bacteria from a dental abscess spreads, it causes an infection of the mouth’s floor. Swelling and severe discomfort are seen beneath the tongue and in the neck. The patient can have trouble breathing in severe circumstances. Ludwig’s angina is a life-threatening disorder. Antibiotics are given to the patients. If breathing problems are present in people with severe Ludwig’s angina, they may need an airway surgery.
- Maxillary sinusitis
The germs spread to the maxillary sinuses, which are tiny cavities behind the cheekbones. This is not a life-threatening condition, although it can be uncomfortable. Fever and sore cheeks are possible symptoms. Sometimes the problem goes away on its own. Antibiotics may be prescribed depending on the seriousness of the infection.
- Osteomyelitis
Bacteria from the abscess may enter the bloodstream and infect the bone. The patient will have a fever, acute pain in the damaged bone, and possibly nausea. The damaged bone is usually close to the abscess’ location. However, because it has migrated into the circulation, it might harm any bone in the body. Antibiotics are given either orally or intravenously.
Treatment for Dental Abscess
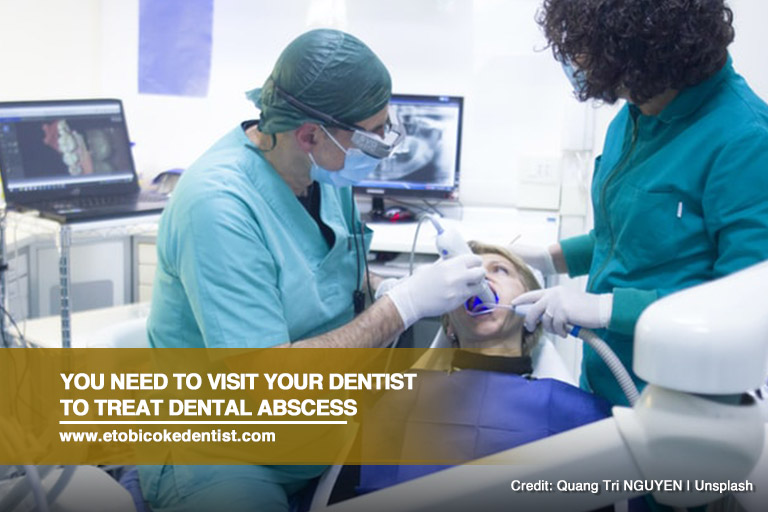
Treatment options for a dental abscess include:
- Antibiotics
Antibiotics for a dental abscess may be administered to prevent the spread of infection. These can be taken in conjunction with pain relievers. If the infection is limited to the abscessed region, you may not need antibiotics, although your dentist may offer them to help with your dental treatment. While this treatment may help fight off leftover bacteria, it will not eliminate the source of the infection, which is the infected tooth.
- Root Canal
A root canal may be necessary to remove the infection and preserve your tooth. This procedure involves removing the affected inner pulp of the tooth and filling the gap with material to avoid infection. After the surgery, your tooth should be restored to normal function. However, you may require a crown to preserve the root canal. The restored tooth can last a lifetime if properly cared for.
- Extraction
Your dentist may have to remove or extract the tooth if it cannot be saved, enabling pus to drain from the socket.
- Surgery
A periapical abscess with a reoccurring infection may require surgical removal of the infected tissue. Additionally, patients who have a periodontal abscess and a reoccurring infection may need their gum tissue remodelled and their periodontal pocket removed.
Don’t neglect dental abscesses. They can turn serious if not treated right away. The infection can spread to your neck, head, and other parts of your body. You’ll need to see a dentist who can save your tooth.
Make regular visits to your dentist and don’t put off regular checks. If you’re in pain, make an appointment with your dentist immediately to get the help you need. For a trusted Etobicoke emergency dentist, call Dr. Mark Rhody Dentistry at (416) 231-4281 now!

